Update 2/22/2022: Great news! The point of this article has been fulfilled because the IRS re-revised Publication 970 for tax year 2021 to reflect the current tax code, which permits taxable graduate student and postdoc income, whether reported on a Form W-2 or not, to be contributed to an IRA.
Publication 970 p. 5 NOW states: “Individual retirement arrangements (IRAs). You can set up and make contributions to an IRA if you receive taxable compensation. A scholarship or fellowship grant is generally taxable compensation only if it is shown in box 1 of your Form W-2, Wage and Tax Statement. However, for tax years beginning after 2019, certain non-tuition fellowship and stipend payments not reported to you on Form W-2 are treated as taxable compensation for IRA purposes. These include amounts paid to you to aid you in the pursuit of graduate or postdoctoral study and included in your gross income under the rules discussed in this chapter. Taxable amounts not reported to you on Form W-2 are generally included in gross income as discussed later under Reporting Scholarships and Fellowship Grants.”
The rest of this article is unchanged from its original publication date on 2/6/2022.
Believe it or not, I look forward to the release of each new version of the IRS’s Publication 970, which covers how fellowship and scholarship income is taxed. I read it thoroughly and make sure that what I teach is in line with it. However, when I opened up the new 2021 version a few days ago, I was disappointed to read on p. 5: “Individual retirement arrangements (IRAs). You can set up and make contributions to an IRA if you receive “taxable compensation” (formerly “earned income”). Under this rule, a taxable scholarship or fellowship grant is compensation only if it is shown in box 1 of your Form W-2, Wage and Tax Statement.” Disappointed doesn’t really touch the depths of my feelings… I was momentarily devastated! I’ve been telling you for over two years now that fellowship income is eligible to be contributed to an IRA regardless of how it is reported or not reported at tax time. Was I wrong? Let’s explore the relevant texts. I have great respect for the IRS publications and find them very useful, but they are not the final word on tax law… the tax code is.

Further reading/listening:
- Fellowship Income Is Now Eligible to Be Contributed to an IRA!
- Do I Owe Income Tax on My Fellowship?
- Weird Tax Situations for Fellowship and Training Grant Recipients
- What Your University Isn’t Telling You About Your Income Tax
- Fellowship and Training Grant Tax Forms
Pre-2020 Status
You must have “taxable compensation” to contribute to an IRA in a given tax year. You can contribute up to the cap for that year ($6,000 in 2019-2022) or your amount of taxable compensation, whichever is lower.
Through tax year 2019, with respect to PhD trainee income, only income reported on a Form W-2 was considered “taxable compensation.”
The text from the 2019 version of Publication 970, Tax Benefits
for Education, reads on p. 5: “Individual retirement arrangements (IRAs). You can set up and make contributions to an IRA if you receive taxable compensation. Under this rule, a taxable scholarship or fellowship grant is compensation only if it is shown in box 1 of your Form W-2, Wage and Tax Statement. For more information about IRAs, see Pub. 590-A and Pub. 590-B.”
Similarly, the text from the 2019 version of Publication 590A, Contributions to Individual Retirement Arrangements (IRAs), reads on p. 6: “Scholarship and fellowship payments are compensation for IRA purposes only if shown in box 1 of Form W-2.”
This text is very clear and reflects the widely held understanding of eligibility for IRA contributions. It was very disappointing for many members of the PhD community; winning a fellowship often comes with a pay raise and therefore an enhanced ability to save for retirement, yet those recipients were barred from making IRA contributions. Keep in mind, these fellowships were taxable as ordinary income, just not considered taxable compensation for IRA contribution purposes. I didn’t like this rule, but I taught it as part of my personal finance material.
The Graduate Student Savings Act
Somehow, the plight of graduate students and postdocs who received fellowship income was heard! The Graduate Student Savings Act proposed to change the definition of taxable compensation. It was put before Congress as a bill in 2016, 2017, and 2019.
An excerpt of the fact sheet for the Graduate Student Savings Act of 2019 reads: “While fellowship or stipend income is taxed by federal and state governments, it doesn’t qualify as “compensation,” meaning that none of a student’s fellowship funds can be saved in an IRA… Many postdoctoral fellows… also receive taxable fellowship income, yet these fellows are also barred from using their fellowship income to contribute to tax-preferred retirement accounts. The Graduate Students Savings Act of 2019 would ensure that any graduate student or postdoctoral fellow who is
paid for their work or their studies can save a portion of their stipend in an IRA.”
While not using super specific or technical language, this excerpt makes clear the intent of the bill: to allow “any graduate student or postdoctoral fellow who is paid for their work or their studies” to contribute to an IRA, i.e., change the definition of taxable compensation.
Graduate Student Savings Act was not successful in being passed as an independent bill in any of those years. Then, in 2019, it was included in the SECURE Act.
The SECURE Act
The Setting Every Community Up for Retirement Enhancement Act of 2019 (SECURE Act) is described by Investopedia as a “far-reaching bill includes significant provisions aimed at increasing access to tax-advantaged accounts and preventing older Americans from outliving their assets.” It was signed into law on December 20, 2019.
The Graduate Student Savings Act was included in the SECURE Act. Here is the relevant text from the bill:
“SEC. 106. CERTAIN TAXABLE NON-TUITION FELLOWSHIP AND STIPEND PAYMENTS TREATED AS COMPENSATION FOR IRA PURPOSES.
“(a) In General.—Paragraph (1) of section 219(f) of the Internal Revenue Code of 1986 is amended by adding at the end the following: “The term ‘compensation’ shall include any amount which is included in the individual’s gross income and paid to the individual to aid the individual in the pursuit of graduate or postdoctoral study.”.
“(b) Effective Date.—The amendment made by this section shall apply to taxable years beginning after December 31, 2019.”
This expands the definition of taxable compensation for the purposes of contributing to an IRA beyond what is reported on a Form W-2. To me, this definition clearly includes taxable fellowship and training grant income paid as stipends and salaries not reported on a Form W-2.
The Tax Code (2021)
From the current Internal Revenue Code section 219 on Retirement Savings, section (f)(1) reads:
“(1) Compensation For purposes of this section, the term “compensation” includes earned income (as defined in section 401(c)(2)). The term “compensation” does not include any amount received as a pension or annuity and does not include any amount received as deferred compensation. For purposes of this paragraph, section 401(c)(2) shall be applied as if the term trade or business for purposes of section 1402 included service described in subsection (c)(6). The term “compensation” includes any differential wage payment (as defined in section 3401(h)(2)). The term “compensation” shall include any amount which is included in the individual’s gross income and paid to the individual to aid the individual in the pursuit of graduate or postdoctoral study.”
Again, I read this as any type of grad student and postdoc salary or stipend with no clauses about being reported on a Form W-2. The language is very similar to how IRS Publication 970 describes fellowship income on p. 5: “A fellowship grant is generally an amount paid for the benefit of an individual to aid in the pursuit of study or research.”
The Internal Revenue Code does seem, to me, to reflect the intent of the Graduate Student Savings Act of expanding the definition of taxable compensation with respect to graduate student and postdoc income beyond what is reported on a Form W-2.
The 2021 Publications
Publication 970
As I stated at the start of this article, Publication 970 disappointingly has not changed its tune on the definition of taxable compensation. It says the same thing in 2021 that it did in 2019 as if the Graduate Student Savings Act had never passed.
Publication 590-A
Publication 590-A, to its credit, now has some mixed language regarding taxable compensation and fellowship stipends and salaries. I’ll compare the 2018 and 2021 versions of this publication.
The 2018 version of Publication 590-A contains exactly one reference to fellowship income on p. 6 in the section titled What Is Compensation?: “Scholarship and fellowship payments are compensation for IRA purposes only if shown in box 1 of Form W-2.”
The 2021 version of Publication 590-A contains this language on p. 6 in the section titled What Is Compensation?: “Scholarship and fellowship payments are compensation for IRA purposes only if shown in box 1 of Form W-2.” So no change there.
However, further down in the same section it says: “Graduate or postdoctoral study. Compensation includes any income paid to you to aid you in the pursuit of graduate or postdoctoral study.”
Are they trying to draw a distinction between “any income paid to you to aid you in the pursuit of graduate or postdoctoral study” and “scholarship and fellowship payments”? What could “any” income mean if not, at least in part, fellowship payments?
To further muddy these waters, Publication 590-A includes Table 1-1, Compensation for Purposes of an IRA. The 2018 version of this table doesn’t mention either fellowship income or graduate or postdoctoral study. The 2021 version lists “taxable non-tuition fellowship and stipend payments” as included in the definition of taxable compensation.
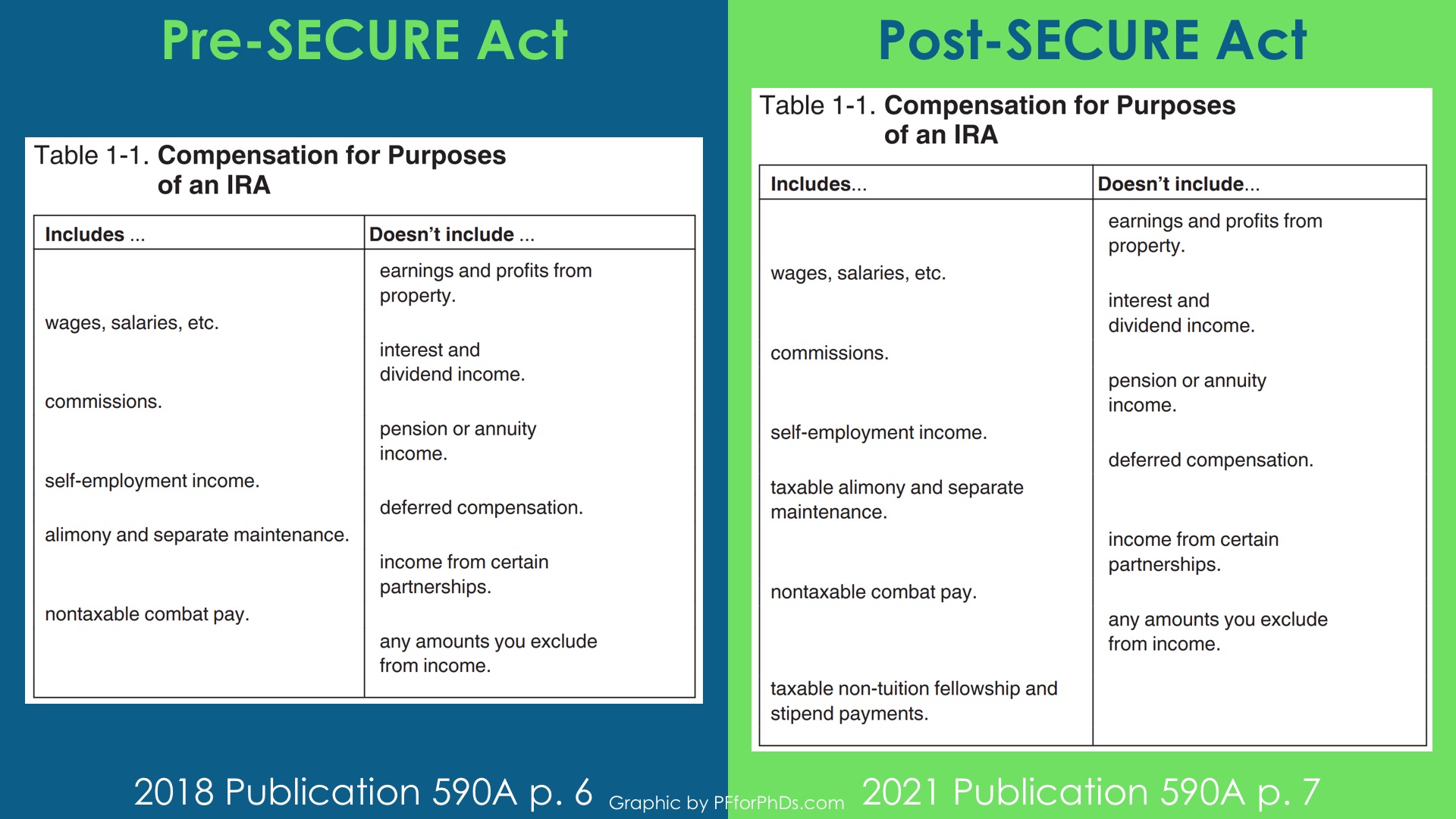
This language in the table is consistent with both employee and non-employee graduate student and postdoc income, again, with no mention of a Form W-2 reporting requirement.
Furthermore, the 2021 version of Publication 590-A says under the Reminders section on p. 2: “Certain taxable non-tuition fellowship and stipend payments. For tax years beginning after 2019, certain taxable non-tuition fellowship and stipend payments are treated as compensation for the purpose of IRA contributions. Compensation will include any amount included in your gross income and paid to aid in your pursuit of graduate or postdoctoral study.”
I am not sure what “certain” means in this paragraph. “Non-tuition fellowship and stipend payments” reads to me as stipend or salary as long as your tuition is being paid by another source of funding. “Any amount included in your gross income and paid to aid in your pursuit of graduate or postdoctoral study” reads to me as both your employee income (reported on a Form W-2) such as from a graduate assistantship position or postdoctoral employee position and taxable non-employee (not reported on a Form W-2), often sourced from a fellowship or training grant.
My Conclusion
My conclusion is that the very clear language in Publication 970 and Publication 590-A excluding taxable fellowship and scholarship income from the definition of taxable compensation unless it is reported on a Form W-2 is not consistent with the spirit of the Graduate Student Savings Act or the current tax code. The changes made by the SECURE Act to the tax code included in the definition of taxable compensation “any amount which is included in the individual’s gross income and paid to the individual to aid the individual in the pursuit of graduate or postdoctoral study.” To me, this means that if you receive a taxable stipend or salary as a graduate student or postdoc, even if it is not reported on a Form W-2, it is taxable compensation for the purpose of contributing to an IRA.
What Do You Think?
I am really struggling with this and I honestly want to know: Do you see a flaw in my reasoning? Is there some difference between “fellowship” and “any income paid… in the pursuit of graduate and postdoctoral study”? Leave a comment here or email me ([email protected]). I am open to the idea that there is something I don’t see or understand. Or let me know if you agree with me.
What Can We Do?
If my argument is valid and the text in IRS Publication 970 and Publication 590A (in part) is incorrect, what can be done? Hit me with your ideas for getting this text updated.
My initial idea is to write to the offices of the Senators (Elizabeth Warren, Mike Lee, Ron Wyden, and Tim Scott) who sponsored the Graduate Student Savings Act to see if they can clarify why the IRS’s language in these publications doesn’t reflect the change the Act brought about. Do you have any other ideas?
The big win for our community was getting the Graduate Student Savings Act passed. The follow-through on that win is making sure that people (and tax software/preparers) know about the change so that graduate students and postdocs can functionally contribute to IRAs.

