One of the most common issues international grad students face when they start grad school in the United States is how to establish credit. The US credit system draws its data only from debts incurred in the US, so whatever credit you had in your home country won’t transfer. Although your options for establishing credit are limited when you first arrive in the US, if you take the right steps, you will build credit quickly.
It’s important to note that in the US your credit is all about debt. The chief reason you want to have good credit is so that you will receive favorable lending terms on any future debt you want to take out. (A secondary reason is that potential landlords and employers sometimes check your credit score to verify your trustworthiness or check for conflicts of interest.) To have good credit, you have to have previously demonstrated that you can manage your debt well. Counterintuitively, having a lot of money to your name or paying your non-debt bills (rent, utilities) on time does not positively affect your credit score. Therefore, to establish your credit for the first time, you have to take out a form of debt, even if that is totally unnecessary for your finances.
What is a credit report and credit score?
A credit report is a list of all the financially-related accounts you have used in the past seven years. There are many different institutions that track this data, but the three main ones are Equifax, Experian, and TransUnion. Your credit report will include data on these accounts, such as how long they have been open, how much outstanding debt you have, and whether you have made any late payments.
A credit score is a number from 300 to 850 that summarizes how ‘credit-worthy’ you are. Another way to say that is how risky it would be for an institution to lend to you. Similarly to the credit report, each credit bureau will calculate its own credit score for you, but they will all be similar as they draw from the same data. A credit score above 750 is considered quite good.

Lenders will look at your FICO credit score, but your attention should be on the accuracy of your credit reports. You can order one free credit report from each bureau once per year through annualcreditreport.com. Once per year (ideally on a 4-month rotation), you should order your credit report from each bureau and check its accuracy. Report any mistakes back to the bureau, and of course if you catch any identity theft, take steps to ameliorate that.
Further reading: “I Want a Credit Card, But I’m Scared”, Don’t Buy the Pro- and Anti-Credit Card Hype
How is my credit score calculated?
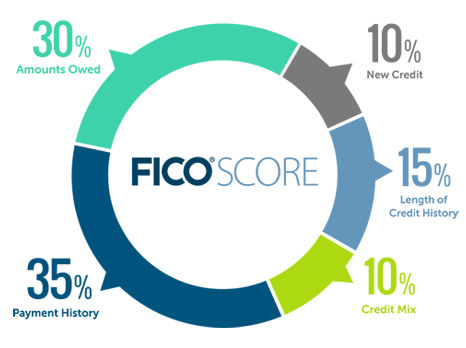
While the exact formula each credit bureau uses to calculate your credit score is proprietary, the components are widely recognized at a general level: payment history (35%), amounts owed (30%), length of credit history (15%), account mix (10%), and new credit (10%).
The way to optimize your credit score is to:
- make every single payment on time
- pay down your outstanding debt
- keep your debt utilization ratio (the percentage of your credit limit that you actually use – both for individual credit cards and all your accounts together) below 30%
- keep your oldest accounts open (e.g., your first regular credit card)
- let time pass (to lengthen your credit history!)
In rare situations, taking out a new, un-needed installment loan for the purpose of increasing your credit score might be a reasonable strategy, but you should conduct heavy-duty research that option before taking such a step (i.e., don’t let a bank representative/salesperson talk you into it).
While applying for new debt will have a small, short-term negative effect on your credit score, you should probably only consciously avoid taking out new debt for this reason in the months leading up to applying for a large loan such as a mortgage.
Further reading: Building Credit as an International Student
How can I establish credit for the first time in the US?
Step 1: Sign up for a secured credit card.
A secured credit card operates similarly to a regular credit card, but the lender holds an asset of equal value to the line of credit extended to you. You give the lender an amount of money (e.g., $500), and that amount is the limit of what you can borrow at a time. Use the secured credit card for purchases, then pay it off on time and in full the way you would a regular credit card (or be charged interest, which only harms you). After several months of using the secured credit card properly, you should have a high enough credit score to qualify for a regular credit card.
Be selective about which secured credit card you sign up for. Community banks and credit unions usually offer better products and customer service than national chain banks. Also examine the annual fee on the card and the interest rate (if there is any possibility of you not paying off the card in full every cycle) to minimize your out-of-pocket costs.
Further reading: What Is a Secured Credit Card? How Is It Different from an Unsecured Card?
Step 2: Close your secured credit card and open a regular credit card.
You can ask your lender to upgrade your secured credit card to a regular credit card, or apply for a new regular credit card and, once approved, close your secured credit card. When you upgrade or close your secured credit card account, your deposit will be refunded (assuming you had no balance due).
Continue to use your credit card perfectly, paying off the balance in full before the due date every month. Keep your utilization ratio low. You will probably have a low credit limit on this first card, so if necessary you can pay off the balance multiple times per month.
You should plan to keep your first credit card open for at least seven years, so choose one without an annual fee, even if it doesn’t offer the most lucrative rewards program.
Further reading: How International Student and Immigrant Workers Can Get a Credit Card
Step 3: Take out an installment loan (e.g., auto loan) or open additional credit cards.
This last step is optional, but helpful for building credit faster. After using your credit card perfectly for several months or a year, your credit score should be increasing gradually. At this point, you are eligible for debt with better lending terms than before.
If you want to buy a car, it should be possible to get an auto loan if you can’t pay for the car outright. If you do take out an auto loan and make payments on time, it will continue to improve your credit score. Similarly, if you open more credit card accounts, your credit score will temporarily dip, but your utilization ratio should also become lower to raise your credit in the long term.
But keep in mind why you are trying to build credit in the first place, and don’t harm yourself (e.g., by paying interest on an unnecessary loan or getting in over your head with credit cards) just for the sake of improving your credit score.
How do I build credit over time?
The best ways to build your credit after you first establish credit in the US are to:
1) Continue to pay all your bills on time and in full.
2) Allow time to pass, which will more firmly establish your track record as a responsible borrower and lengthen your credit history.
3) Pay down outstanding installment loans (though not necessarily off completely) and keep your credit utilization ratio low. (It is a myth that you have to carry a balance from month to month on your credit card for it to improve your credit score; in fact, this strategy will depress it.)
International students are not the only graduate students without credit; some domestic students who have avoided student loans and credit cards face the same issue. Just keep in mind your ultimate goal that motivates your desire to establish credit (e.g., qualify for a lease, borrow money for a car at a good interest rate), and don’t take unnecessarily extreme steps with your borrowing simply to achieve a high score. Making on-time payments, holding on to minimal amounts of debt, and time are the best boosters to your credit score.
Join Our Phinancially Distinct Community

Receive 1-2 emails per week to help you take the next step with your finances.


[…] Further reading: How to Establish Credit in the US […]